Mining is an essential industry that has played a significant role in shaping human civilization. From ancient times to the modern era, mining has been instrumental in extracting valuable minerals, metals, and resources from the Earth’s crust to meet the ever-growing demands of industry and society. However, the methods employed in mining have evolved over time, each with its unique set of advantages and drawbacks. This article delves into a few key mining methods, highlighting their impact on the environment, communities, and the global economy.
Introduction to Mining Methods
Mining methods can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: surface mining and underground mining. Surface mining involves the removal of overburden (soil, rock, and other materials) to access the ore or mineral deposit. In contrast, underground mining involves digging tunnels and shafts to reach the deposit beneath the Earth’s surface. Both methods have distinct advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on various factors, including the type of deposit, depth, location, and environmental considerations.
Surface Mining
Surface mining encompasses several techniques, such as open-pit mining, strip mining, and mountaintop removal mining. These methods are often used for extracting resources like coal, copper, gold, and aggregates. They are characterized by their ability to extract large quantities of ore efficiently but can have significant environmental and social impacts.
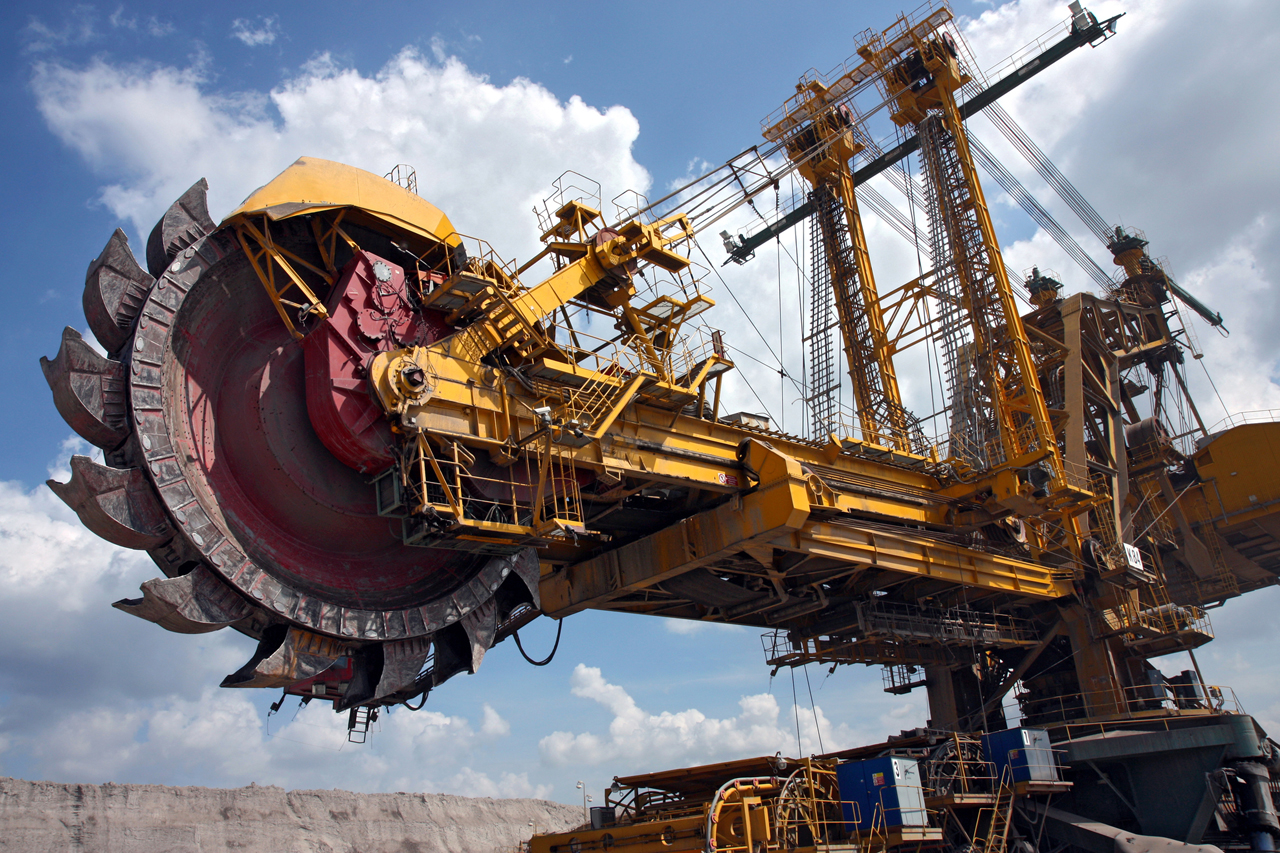
Open-Pit Mining
Open-pit mining is one of the most common surface mining methods. It involves the excavation of a large, open pit or quarry to access valuable minerals or ores. This method is cost-effective and can be used for a wide range of deposits. However, it often results in substantial land disturbance, habitat destruction, and the generation of large waste piles. Additionally, open-pit mines can consume vast amounts of water for mineral processing and dust suppression, which can strain local water resources.
Strip Mining
Strip mining is another surface mining technique commonly used for coal and some metal ores. In strip mining, successive parallel cuts or “strips” are made in the Earth’s surface to access the underlying deposit. This method can be more efficient than open-pit mining in some cases but has similar environmental concerns, such as land disturbance and water usage. Strip mining can also lead to soil erosion and negatively impact local ecosystems.
Mountaintop Removal Mining
Mountaintop removal mining is a highly controversial form of surface mining that is primarily used for coal extraction in hilly or mountainous areas. It involves the removal of mountaintops and the disposal of excess material in valleys and streams. This method has severe environmental consequences, including the destruction of entire ecosystems, water pollution, and health risks for nearby communities due to dust and water contamination. Mountaintop removal mining is a subject of intense debate and regulatory scrutiny due to its devastating impact on the environment and local communities.
Underground Mining
Underground mining methods, on the other hand, involve creating tunnels and shafts to access mineral deposits deep beneath the Earth’s surface. This approach is often used when the ore body is too deep, or when surface mining is not feasible due to environmental or logistical constraints. Underground mining methods include room and pillar mining, block caving, and longwall mining.
Room and Pillar Mining
Room and pillar mining is a technique where rooms (openings) are created within the ore body while leaving behind pillars of ore to support the roof. This method is commonly used for coal, salt, and some metal ores. While it minimizes surface disruption, it can result in significant subsidence (sinking of the land above the mined area) and can be inefficient for extracting low-grade deposits.
Block Caving
Block caving is a method used for massive ore bodies that are too deep for open-pit mining. It involves the controlled collapse of an ore body from beneath, creating a cavity where the ore can be collected. Block caving is highly efficient but can result in surface subsidence, making it unsuitable for areas with infrastructure or communities on the surface.
Longwall Mining
Longwall mining is a high-tech underground method used for coal extraction. It employs a mechanical shearer that cuts long panels of coal from the underground seam. This method is efficient and minimizes surface disruption, but it can lead to ground subsidence and has potential environmental challenges, such as water management and air quality control.
Impact of Mining Methods
The choice of mining method has far-reaching consequences, impacting various aspects of the environment, society, and the economy.
Environmental Impact
All mining methods, whether surface or underground, have the potential to cause environmental harm. Surface mining methods often result in the destruction of ecosystems, soil erosion, water pollution, and the release of greenhouse gases. Underground mining, while minimizing surface disturbance, can still lead to subsidence, groundwater contamination, and the release of hazardous substances.
For example, mountaintop removal mining in Appalachia has caused the loss of entire forests, streams, and aquatic habitats. The removal of mountaintops and subsequent valley filling can disrupt natural drainage patterns, leading to severe flooding downstream. Additionally, the release of heavy metals and pollutants from mining operations can harm aquatic life and pose health risks to nearby communities.
Social Impact
Mining also has significant social implications. The communities surrounding mining operations often experience both positive and negative effects. On the one hand, mining can create jobs, stimulate local economies, and provide revenue to governments through taxes and royalties. On the other hand, it can lead to the displacement of communities, social unrest, and health issues due to exposure to pollutants and unsafe working conditions.
Indigenous communities are frequently among the most affected by mining activities, as their traditional lands often overlap with resource-rich areas. Disruption of these communities’ way of life and the degradation of their environment can have lasting social and cultural consequences.
Economic Impact
Mining plays a crucial role in the global economy, providing essential raw materials for various industries. It contributes significantly to GDP and export earnings in many countries. However, the economic impact of mining can be volatile, as it is closely tied to commodity prices and market demand. Economic downturns in the mining sector can lead to job losses and economic instability in mining-dependent regions.
Environmental Mitigation and Responsible Mining Practices
Recognizing the environmental and social challenges associated with mining, there is a growing emphasis on responsible mining practices and environmental mitigation measures. These include:
- Reclamation: After mining operations cease, companies are increasingly required to restore the land to its original or an equivalent state. This may involve regrading, replanting, and creating sustainable land uses.
- Water Management: Implementing measures to minimize water use and pollution is crucial. Techniques like zero-discharge systems and water recycling can reduce the environmental impact.
- Community Engagement: Mining companies are encouraged to engage with local communities, respecting their rights and addressing concerns. This can include job training, community development projects, and revenue-sharing agreements.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs): Rigorous EIAs are essential to evaluate the potential environmental effects of mining projects and determine appropriate mitigation measures.
- Technological Advancements: The development of cleaner, more efficient mining technologies and processes can reduce the environmental footprint of mining operations.
- Regulation and Oversight: Governments play a crucial role in regulating mining activities and ensuring compliance with environmental and safety standards.
Mining is an integral part of modern society, providing the raw materials necessary for countless industries. However, the choice of mining method and the way it is practiced can